Harness the Power of IIoT in Manufacturing

In modern manufacturing, staying ahead requires more than efficiency—it demands innovation. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming the industry by enabling smart, connected systems where machines communicate, make real-time decisions, and optimize operations. While both IoT and IIoT focus on connectivity, the difference between IoT and IIoT lies in their application; IoT enhances consumer experiences, while IIoT is built for industrial environments, prioritizing reliability, security, and large-scale efficiency.
Industrial IoT seamlessly integrates cutting-edge technologies with traditional manufacturing processes, opening doors to unprecedented levels of automation, data-driven decision-making, and real-time insights. As we embark on this transformative journey, this blog will delve into the intricacies of Industrial IoT in manufacturing, exploring its applications, benefits, and profound impact on optimizing operations and driving businesses toward a future where innovation meets productivity. Let’s unravel the potential of Industrial IoT and its role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Understanding IIoT
IIoT refers to the interconnected network of sensors, devices, machines, and systems within the industrial setting. It enables data collection, analysis, and exchange, facilitating intelligent decision-making and enhancing overall operational efficiency in manufacturing. Manufacturers globally now recognize the disruptive potential of IIoT. According to a Research and Markets study in 2022, the estimated market value of IoT in manufacturing was $209.44 billion globally. The market value is forecasted to reach $397.86 billion by 2026 at a 17.4% CAGR. (emsnow)
It is anticipated that the revenue will exhibit a CAGR of 2024-2028 of 16.53%, resulting in a market volume of ₹US$21.78bn by 2028.(statista) India's industrial IoT market is witnessing rapid growth driven by government initiatives and the increasing adoption of smart manufacturing technologies.
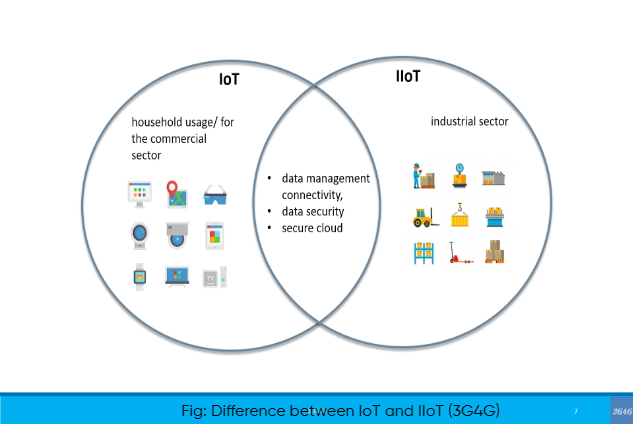
What is the difference between IoT and IIoT?
While the IoT and IIoT share various technologies like cloud platforms, sensors, connectivity, machine-to-machine communications, and data analytics, they serve distinct purposes.
IoT systems link devices across diverse sectors, including agriculture, healthcare, enterprise, consumer, utilities, government, and cities. The technology behind IoT encompasses smart devices, fitness bands, and other applications that typically don't pose emergency risks if something goes wrong.
In contrast, IIoT applications establish connections between machines and devices in the oil and gas, utilities, and manufacturing sectors. Failures and downtime in IIoT deployments can lead to high-risk or life-threatening situations. Furthermore, IIoT applications prioritize improving efficiency, health, or safety, differing from the user-centric focus of IoT applications.
What are the critical components of IIoT in manufacturing?
Key components of IIoT include sensors, devices, and machines that collect and transmit data. Integrating these components in an industrial setting enables the creation of a connected ecosystem, fostering seamless communication and data exchange.
The critical components of IIoT in manufacturing are pivotal in establishing a robust and interconnected infrastructure that facilitates seamless data flow. Understanding these components is essential for harnessing the full potential of IIoT. Let's delve deeper into each component:
Sensors: Sensors are at the heart of IIoT, serving as the eyes and ears of the connected ecosystem. These small, specialized devices are embedded in machinery and equipment to capture real-time data from the physical environment. Various sensors, such as temperature, pressure, motion, and proximity, are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing facility. These sensors continuously monitor and gather information on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and production processes.
Devices: IIoT devices act as the interface between the physical and digital realms. These devices receive sensor data and transmit it to the central processing unit for analysis. Examples of IIoT devices include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), industrial gateways, and edge computing devices. PLCs, for instance, are crucial for controlling and automating manufacturing processes. Industrial gateways facilitate communication between devices and the cloud, ensuring a seamless data exchange. Additionally, edge computing devices enable data processing at the network's edge, reducing latency and improving overall system efficiency.
Machines: The machines in a manufacturing setting are not merely standalone entities but integral components of the IIoT ecosystem. Modern manufacturing machines, including special purpose machines, have embedded sensors and communication interfaces, enabling them to contribute to the data pool. These machines can transmit operational data, production metrics, and performance analytics. Integrating special purpose machines into the IIoT framework provides a holistic view of the production process, enabling better decision-making and optimization.
Data Processing and Analytics Platforms: Once data is collected from sensors, devices, and machines, it must be processed and analyzed to extract meaningful insights. Often integrated with cloud computing services, data processing platforms handle the vast amounts of information IIoT components generate. Advanced analytics tools, including machine learning algorithms, derive actionable intelligence from the data. This analysis enables predictive maintenance, process optimization, and data-driven decision-making.
Let’s review some benefits of implementing IIoT in your manufacturing processes.
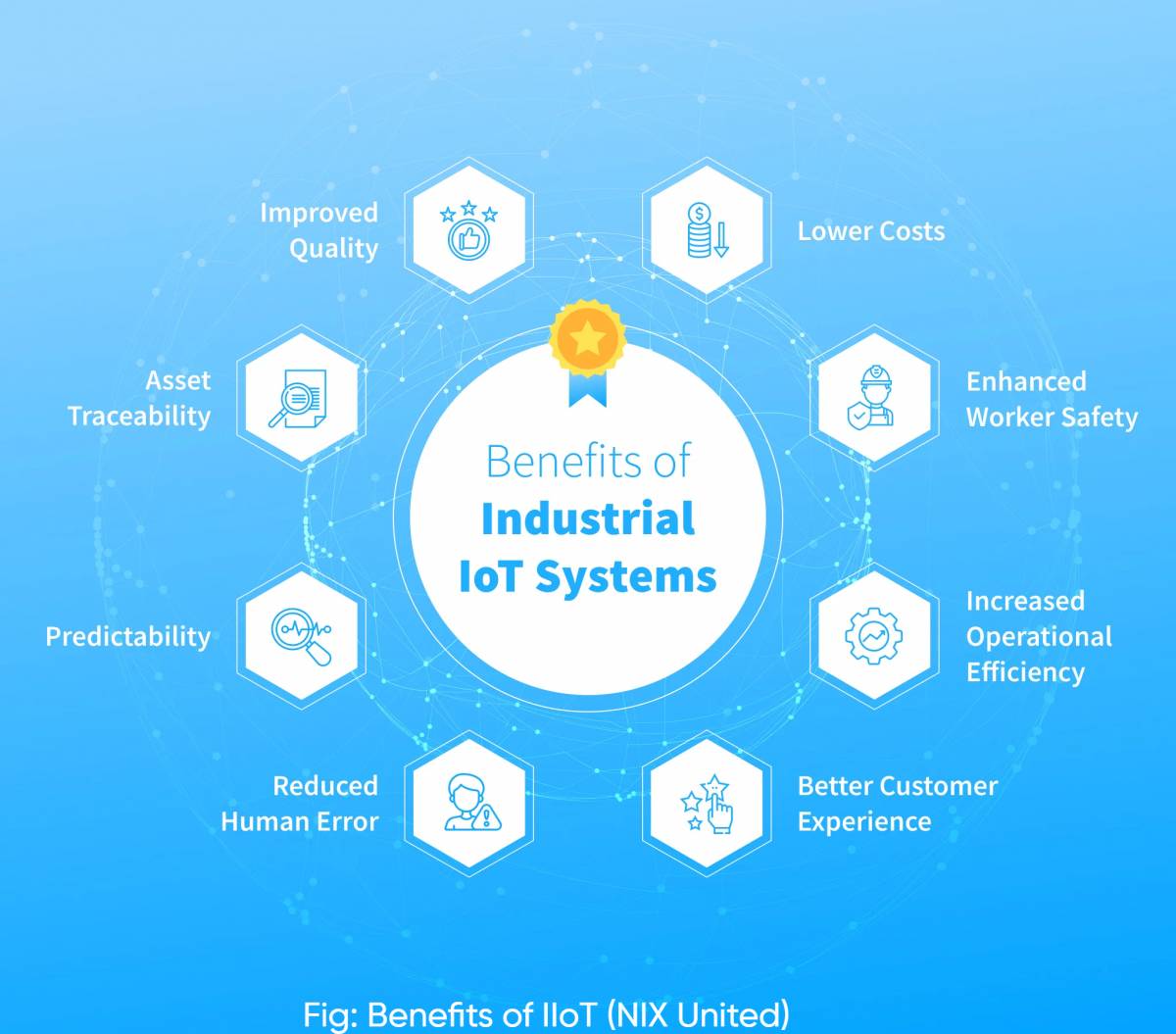
Benefits of IIoT in manufacturing
The benefits of IIoT in manufacturing are multifaceted, revolutionizing traditional processes and fostering a new era of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. Here's an in-depth exploration of the key advantages:
Increased Operational Efficiency:
IIoT enables real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, optimizing operational efficiency. By integrating sensors and devices, manufacturers gain unprecedented visibility into production workflows. This real-time data allows for quickly identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and deviations from optimal conditions. As a result, processes can be adjusted on the fly, minimizing downtime and maximizing overall efficiency.
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization:
The data-driven insights provided by IIoT contribute to substantial cost savings and resource optimization. Manufacturers can identify areas of waste, energy consumption, and inefficiencies in the production chain. By making informed decisions based on actionable data, organizations can reduce operational costs, minimize resource usage, and enhance overall sustainability.
Improved Quality Control and Product Traceability:
IIoT ensures product quality and traceability. Manufacturers can continuously monitor production processes by identifying deviations from quality standards in real-time. This enables proactive intervention to address issues before they escalate, reducing the likelihood of defective products reaching the market. Additionally, IIoT facilitates end-to-end product traceability, allowing manufacturers to track the journey of raw materials, components, and finished products throughout the supply chain.
Enhanced Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime:
IIoT's predictive maintenance capabilities transform traditional maintenance practices. By continuously monitoring the condition of equipment and machinery through embedded sensors, manufacturers can predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime, extends the lifespan of machinery, and reduces the overall maintenance cost. Predictive maintenance schedules are optimized based on usage and performance data, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently.
Facilitated Regulatory Compliance:
In industries with stringent regulatory requirements, IIoT ensures compliance. By automating data collection and reporting processes, manufacturers can easily demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards. This helps avoid fines and penalties and enhances the organization's reputation regarding safety, quality, and environmental compliance.
Increased Productivity and Output:
IIoT's ability to optimize processes, reduce downtime, and enhance resource utilization directly increases productivity. Manufacturers can achieve higher production volumes without compromising quality by automating routine tasks, providing real-time insights, and facilitating data-driven decision-making.
Improved Operator Safety and Ergonomics:
IIoT technologies enhance operator safety by monitoring environmental conditions and identifying potential hazards. Wearable devices equipped with sensors can track operator movements and provide real-time alerts in case of unsafe conditions. Additionally, IIoT supports the implementation of ergonomic improvements based on data insights, promoting a safer and healthier working environment.
Faster Time-to-Market: With IIoT, manufacturers can accelerate product development cycles and bring new products to market faster. The ability to quickly gather and analyze data throughout the product lifecycle enhances innovation and allows organizations to respond swiftly to market trends and customer preferences.
The benefits of IIoT in manufacturing extend beyond operational improvements to influence the entire value chain. By harnessing the power of real-time data and connectivity, manufacturers can optimize their current processes and lay the foundation for future advancements and sustained competitiveness in a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
Challenges and Solutions in IIoT Implementation
IIoT brings many opportunities and unique challenges. Navigating the complexities of implementing IIoT in a manufacturing environment requires a nuanced understanding of potential obstacles and, more importantly, effective strategies for overcoming them. Let’s delve into the key challenges industries face embracing IIoT and explore innovative solutions that pave the way for a seamless and secure integration. From addressing security concerns to ensuring interoperability, this segment provides insights into navigating the intricate landscape of IIoT implementation.
Security Concerns in IIoT
Challenge: The interconnected nature of IIoT systems poses cybersecurity risks, including unauthorized access and data breaches.
Solution: Implement robust encryption and secure communication protocols, and conduct regular security audits to fortify the IIoT infrastructure against cyber threats.
Interoperability Issues
Challenge: Compatibility issues arise when integrating diverse sensors, devices, and machines from different manufacturers.
Solution: Adopt standardized communication protocols and promote industry-wide collaboration to ensure seamless interoperability.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Challenge: Collecting and processing sensitive data raises privacy and regulatory compliance concerns.
Solution: Establish stringent data access controls, anonymize personal information, and adhere to relevant data protection regulations to maintain compliance.
The dynamic nature of IIoT requires ongoing strategies to address emerging challenges and technological advancements. It is crucial to stay updated on cybersecurity trends, invest in employee training, and remain agile in adopting new technologies to proactively address evolving challenges.
Real-world Applications of IIoT in Manufacturing
IIoT has ushered in a new era of smart manufacturing, where connectivity and data-driven insights converge to enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. Across diverse sectors within manufacturing, IIoT applications are making a tangible impact. Let's explore some compelling real-world applications:
Smart Factories and Production Lines
Application: IIoT transforms traditional factories into intelligent ecosystems where machines, sensors, and devices collaborate seamlessly. Automated processes, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring characterize smart factories, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Supply Chain Optimization
Application: IIoT enables a holistic view of the supply chain by providing real-time data on inventory levels, production schedules, and logistics. This visibility allows manufacturers to optimize procurement, minimize lead times, and improve supply chain responsiveness.
Quality Assurance through Data Analytics
Application: IIoT-driven data analytics ensures continuous monitoring of production processes. Manufacturers can promptly identify deviations from quality standards by collecting and analyzing data in real-time, enabling proactive interventions to maintain product quality.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Application: IIoT enables remote monitoring and control of manufacturing processes. Supervisors can oversee operations from anywhere through connected devices and applications, making real-time adjustments, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring continuity even without physical presence.
These real-world applications underscore the transformative potential of IIoT in manufacturing. As industries continue to embrace and refine these applications, the manufacturing landscape is evolving into a highly connected, intelligent, and responsive ecosystem, paving the way for unprecedented advancements in efficiency, quality, and innovation.
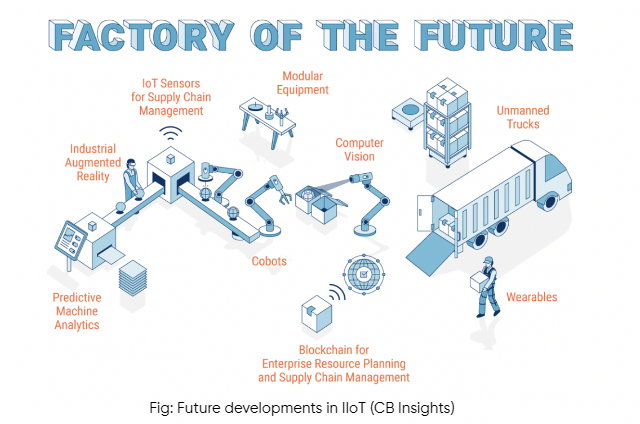
Future developments in IIoT for manufacturing
The future of IIoT in manufacturing is expected to bring significant advancements and transformations in various aspects. Some of the key future developments and trends in IIoT for manufacturing include:
Connectivity Technologies:
The future of IIoT in manufacturing will rely heavily on advanced connectivity technologies to enable seamless communication between machines, sensors, and software systems, improving efficiency and productivity.
Predictive Maintenance and Analytics:
AI-powered analytics will enable manufacturers to gain deeper insights from the vast amounts of data generated by IIoT devices, leading to better decision-making and predictive maintenance.
Automated Inventory Management:
IIoT can help manufacturers monitor stock levels in real-time, optimize inventory management, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Quality Control Advancements: IIoT is driving advancements in quality control by monitoring and analyzing production processes in real-time.
Sensor Advances and Innovations:
Sensor Advances and Innovations: The market for industrial automation sensors is projected to reach $22.59 billion by 2029, driven by the rising adoption of Industry 4.0 and IIoT in manufacturing. (researchandmarkets)
5G Sensor Capability:
Integrating 5G technology with IIoT devices will enable faster and more reliable communication, leading to improved performance and cost savings in the manufacturing processes.
These future developments in IIoT for manufacturing will help unlock new possibilities for automation, remote monitoring, and real-time decision-making, ultimately leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in the manufacturing industry.
Embrace IIoT and Transform Your Business
IIoT is no longer a futuristic vision but a tangible force reshaping the manufacturing landscape. By integrating smart sensors, data analytics, and connected devices, businesses can unlock a new operational efficiency, agility, and sustainability era.
Embrace IIoT and witness a transformation: predict maintenance issues before they arise, personalize products on the fly, and respond to market shifts with laser-sharp precision. Real-time data becomes your guiding light, illuminating opportunities for optimized processes, reduced downtime, and enhanced quality control.
While challenges like cybersecurity and workforce upskilling exist, they are hurdles, not roadblocks. At Titan Engineering and Automation Limited (TEAL), a thriving ecosystem of solutions and seasoned consultants eagerly awaits to guide your implementation journey. Explore our blog on 'How TEAL is leveraging IIoT in automation to create smart factories' for a clear insight into how we can assist in transforming your business. Take the initial step with pilot projects and experience firsthand the transformative power of IIoT.
It’s time to lead the IIoT revolution. Invest in your future, embrace the connected factory, and watch your business soar.
Frequently Asked Questions
